Redirected Walking in 360° videos
Use natural walking to control the playback of 360° videos
Intro
Most 360° video-based applications typically require users to stay in a fixed position, such as sitting while watching a panoramic video. This discrepancy between bodily perception and visual input hinders immersion and can lead to motion sickness (also known as simulator sickness, or SS).
Using natural walking to control the playback of the 360° videos is a realistic and immersive way to matches visual and self-motion perception. Redirected walking (RDW) techniques can enable users to walk in limited physical tracking space but experience larger scenes.
In this project, we utilized RDW technique to establish a VR system use natural walking to control the playback of the 360° video, making users believe they “physically” walk in the scene of the 360° video.

System Design
Our system’s core concept is to allow users to physically walk in a normal tracking space while experiencing scenic areas through watching 360° videos on a VR headset.
In panoramic videos capturing scenic areas, the camera’s movements can be simplified as a combination of linear motion and stationary turns. When users watch these panoramic videos in a VR headset, this VR system guides them to follow the same path as the camera’s movements. This synchronization of users’ physical perception and visual information gives them the sensation of actually walking in the real scene captured by the 360° videos.
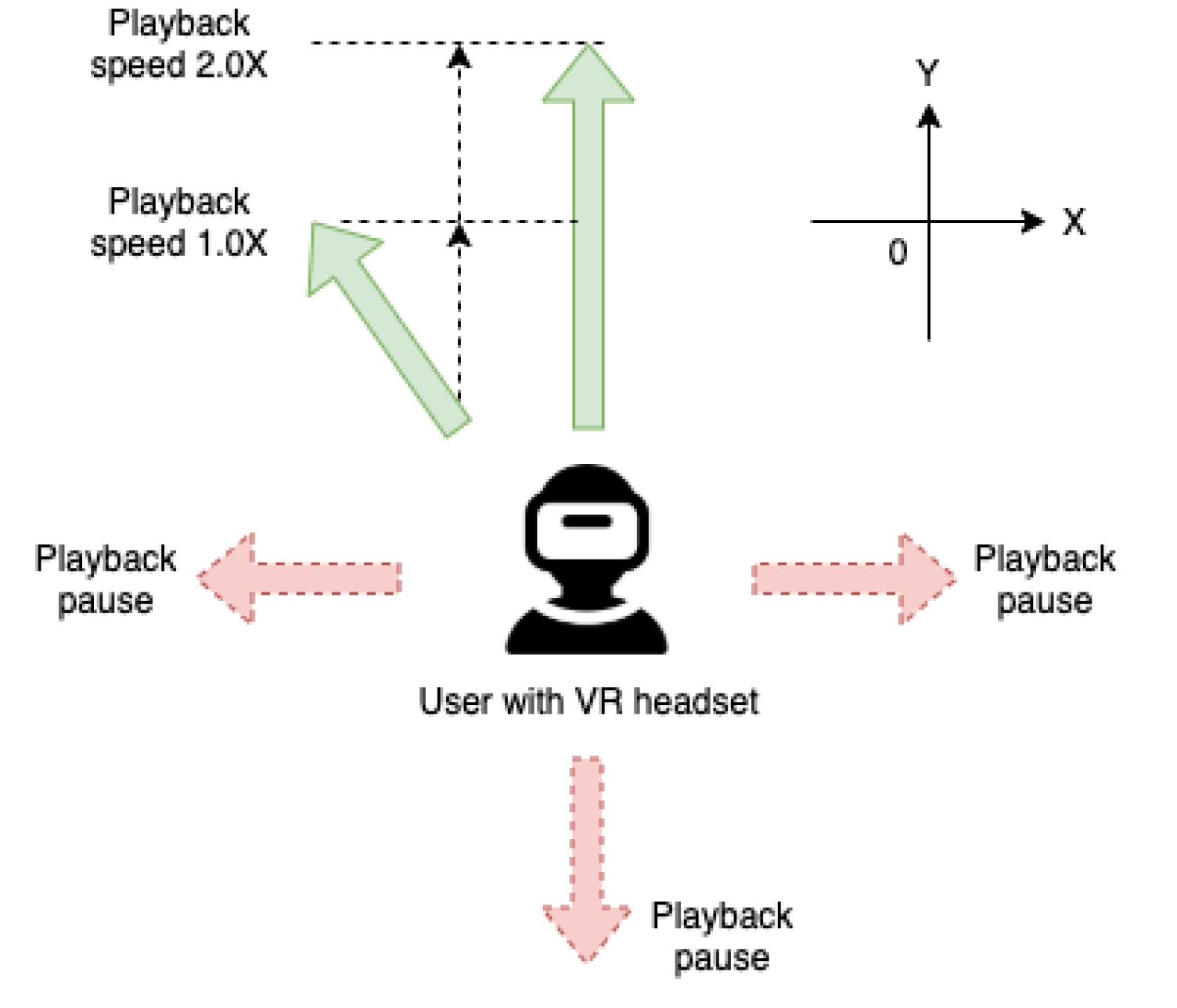
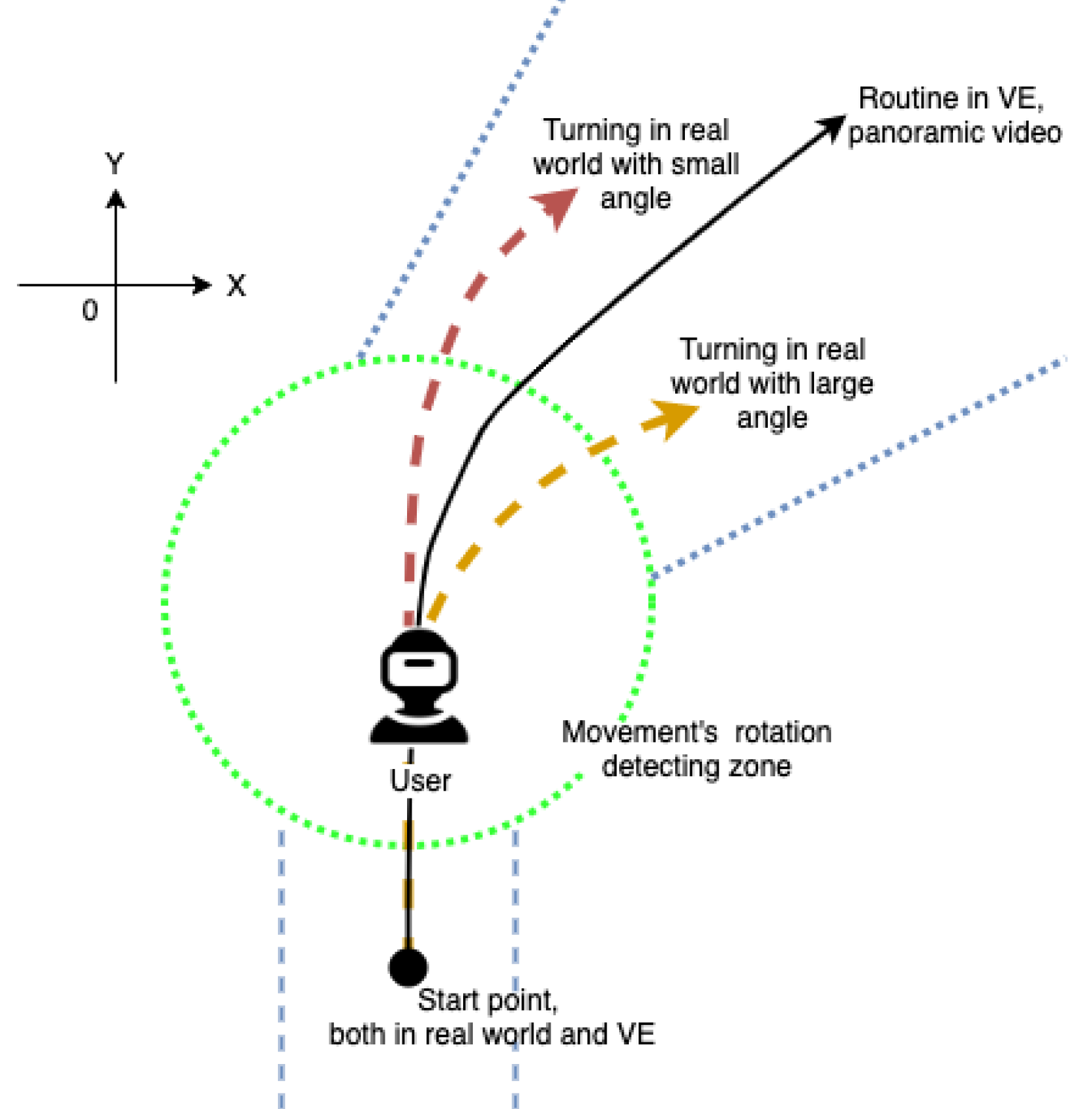
During linear camera movements in the panoramic videos, the VR system adjusts the playback speed based on the velocity component in the direction of camera movement as detected by the user’s VR headset. When there are turns, the VR system instructs the users to remain stationary and control the playback of the panoramic videos by detecting the rotational movement of the headset.
User Study
We conducted a user study about the detection thresholds for translation (N = 20) and rotation gains (N = 18) in 360° video-based virtual environments in three scenes with different widths (3m, 20m and 100m). The results can be used as design references for immersive 360° video-based natural walking applications.[1]
Demo
Next, we will develop a systematic tool for converting 360° videos into immersive VR natural walking tours. With this tool, users will have the flexibility to select their preferred 360° videos and customize their touring experiences based on their individual interests.
(Expect multiple updates in the next weeks.)
References
[1] ZHANG Y, LIU Q, WANG Y. Redirected walking in 360° video: effect of environment size on detection thresholds for translation and rotation gains[C]//2022 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (VRW). 2022: 830-831. DOI:10.1109/VRW55335.2022.00266.